Neutron Supply
The characteristics of the neutron source depend on the
applications.
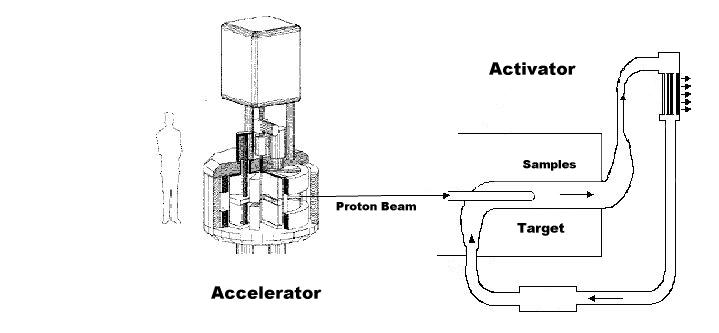
The application for medical purposes (The Activator ) demands small neutron intensities, and fortunately, many different types of compact neutron sources are commercially available.
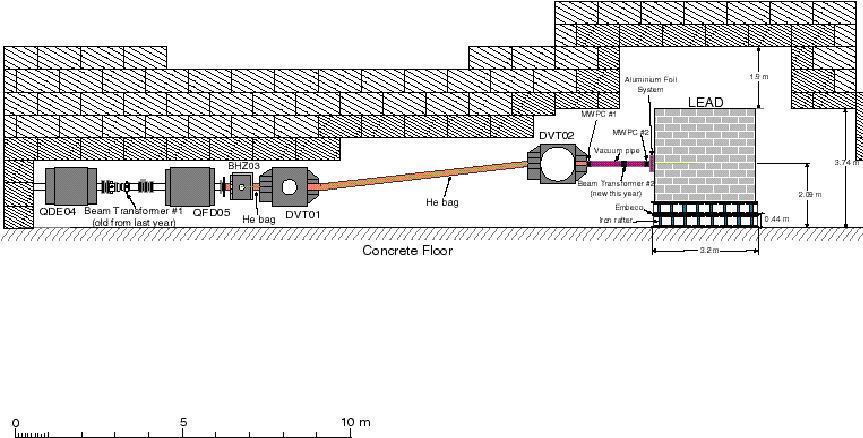
The application for environmental purposes (The Waste Transmuter ) needs a much stronger neutron source since the sample must undergo a complete transformation into stable elements. So, it would be necessary a spallation source like 2.b (as shown in the figure), or, even better, a source of neutrons from the spent fuel of a typical Light Water Nuclear Reactor (LWR).
Home Back
The application for medical purposes (The Activator ) demands small neutron intensities, and fortunately, many different types of compact neutron sources are commercially available.
1. Radioactive sources: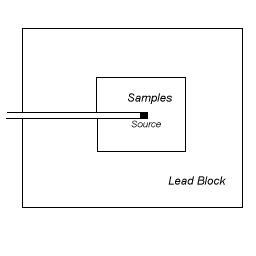
a. Alfa particle sources like Am-Be and similar, which produce about 2 x 106 neutrons / Curie of the a-source.
b. Actinide sources like 252 Cf which spontaneously fissions producing about 3 x 109 n/Cie.
This type of sources are much more modest than accelerators but their advantages are simplicity and lower cost.
2. Accelerators
a. Small accelerators like Cyclotrons or Linear Accelerators (LINACS), producing typically about 1013 neutrons/ sec.
This type of accelerators (producing energies in the order of Mev) are already widely used in hospitals for isotope production, for instance for PET applications.
b. Spallation sources from high energy proton beams hitting a Lead target block (a very prolific neutron source, 1016 n/sec are easily obtained). This high-energy source (200 MeV Cyclotrons or LINACS) will be interesting in a large industrial scale. See figure.
The application for environmental purposes (The Waste Transmuter ) needs a much stronger neutron source since the sample must undergo a complete transformation into stable elements. So, it would be necessary a spallation source like 2.b (as shown in the figure), or, even better, a source of neutrons from the spent fuel of a typical Light Water Nuclear Reactor (LWR).

Home Back