6th step
: 01 : : 02
: : 03 : : 04 : : 05
: : 06 : : 07 : : 08
: : 09 : : 10 :
identification of particles from a collision by their decays
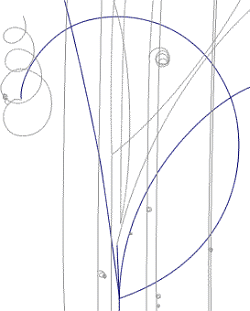
We have seen how an unstable neutral particle can be identified via its decay into two oppositely charged particles.
An unstable charged particle may also decay - usually into a charged
particle of the same sign and one or more neutral particles. This shows up in the
bubble chamber as a kink - a sudden change into a more curved track (move
cursor ![]() above the picture).
above the picture).
Notice that one of the positive tracks kinks twice, ending up with a
positive spiraling track, produced by an anti-electron ![]() .
(Only
.
(Only ![]() and ordinary electrons
and ordinary electrons ![]() will spiral).
will spiral).
The number of unstable particles that travel (more details...) far enough to decay in the bubble chamber is limited. They leave characteristic decay signatures that enable the parents to be identified.