
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Apparatus:
RADIOACTIVE SAMPLE, device for
detecting and measuring radiation, piece of paper, piece of aluminum,
piece of lead
Method:
First measure the rate of decay of the sample's background (table,
air) in order to make our experiment more precise. This value will be later
subtracted from the measured decay rate of a sample so you will get the
exact value of its radiation. Then start to measure g , (b + g )
and (a +b + g ) decay rates with the following procedure:
1) (a +b + g ) decay will be measured
directly ( there are no barriers between sample and detector)
2) As soon as you put a sheet of paper between
them, you are able to measure only the values of (b + g ) decay since the
a decay is not able to penetrate the paper.
3) When you put a piece of aluminum between
then sample and the detector, only g decay will be measured. The
a and b decay can't pass through the aluminum.
Repeat this procedure 20 times, waiting 2 minutes between each set of three measurements. Having done the measurements you obtain the values of number of decays per second . You are able to construct three graphs of (a +b + g ), (b + g ) and g decay, plotting the amount of decay against time. For each graph you subtract the base value decay rate represented by the straight line.
You could easily calculate the half life time of our radioactive sample from your graph.
Apparatus:
Neon Franck-Hertz tube - Leybold
didactic GMBH, power source, voltmeter, ammeter, rheostat, wires
Introduction:
In 1914, James Franck and Gustave Hertz demonstrated that an atom may
be raised from the ground to an excited state by other than electromagnetic
radiation. For example, in a collision of an electron with an atom, the
latter may be excited provided that initial energy of the electron is at
least equal to the energy difference between the excited and ground states
of the atom. Since Franc and Hertz obtain values for different excitation
energies, which were integral multiples of the first excitation energy,
they confirmed Bohr's idea of quantized energy levels in atom.
Method:
1) You set up an electric circuit similar to that
in fig.1
2) You gradually increase the accelerating voltage
V1 by 2 V . After each increase you notice the current I and voltage V
3) Make a graph of current versus grid potential.
4) You observe the number of light strips radiated.
Notice:
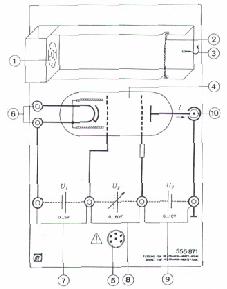
1) Cathode heater
2) Cathode
3) Projective cylinder
4) Control cylinder
5) Acceleration grid
6) Target electrode
Low-pressure tube with electrode system filled with neon: approx. 10hPa
Heating voltage Vf :
6.3 V ( approx. 260 mA)
Control voltage V1 between
cathode and control grid:
5 V
Acceleration voltage V2 between
control grid and acceleration grid:
0...80 V
Counter voltage V3 between
acceleration grid and target electrode:
0...10 V
Excitation level of the Ne-atoms:
16-18 eV
Apparatus:
20 match- boxes, each contains a number of unknown objects, scales
Introduction:
Robert Millikan was the first who to determine the value of the elementary
charge on the electron. He provided this by famous oil-drop experiment
in which he presented convincing evidence that any charge measured was
an integral multiple of a smallest charge e. This led to the theory of
quantization of electric charge. This experiment attempts to use the method
of quantization in finding out the mass of the "'quantum'' - in our case
the mass of an unknown object placed in the match- box. Of course, our
investigation is not so thorough as Millikan's since we are dealing with
only 20 match-boxes. However, the approach to the problem is the same.
Method:
The measurement of the objects' mass must be done indirectly since
it is our restriction that they cannot be examined individually and the
boxes must remain unopened. We already know that the objects are grouped
in whole numbers but we do not know how many objects are in each box. We
don't know the mass of the boxes, but we can assume that they are approximately
the same. The mass of one box is less than the mass of the lightest contents.
Being aware of all the restraints, and knowing the facts described above
we follow this procedure:
1. Find and record the mass of each of the boxes and
their contents.
2. Plot a histogram of the number of times a mass
is observed versus the mass value
3. Work out a value for the object mass (The reasoning
is given in Calculations)
4. Identify how many objects are in each box
5. Determine the mass of the match- box
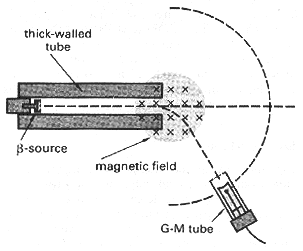
A beta source (probably strontium) is pointed at a GM tube about 30cm away but with no magnetic field present. The beam gives a fairly sharp readout at the direct position, and if the gm tube is rotated as shown on the diagram, the counts fall away rapidly.
A magnetic field is now placed with the field lines vertical. Magnadur magnets are ideal and give a strong field for their size, or an electromagnet can be used. Beta particles are now detected at an angle, away from the straight-on direction, in a direction consistent with a negative charge (but remember that if this is decided by Fleming's Left hand Rule, the 'current' is flowing TOWARDS the source). The angle will typically be around 30û, although the beta particles will have a range of kinetic energies and so the deflected beam will not have a sharply defined direction.
Reversing the field reverses the deflection. An electromagnet will allow the magnitude of deflection to be changed.
This will not produce an observable effect with alpha particles. The mass is so large that the deflection is too small to be measured with basic school apparatus.
| Contact: Hanley@southbridge.demon.co.uk | Last modified: 6.9.99 |